gasadmin tool
The gasadmin tool is provided as an administrative command for the Genero Application Server.
- Manage sessions
- GAS administration
- GAS configuration
- Manage GBC
- Manage application archives
- Monitor web services
- Manage services
- Manage applications
Syntax
gasadmin { -V | -h | command [ options ] [ args ] }- Display help or version information for the gasadmin command. Help is specific to commands and there is a help option for each command.
- command. There are various commands to administer the GAS:
- session — Administer application sessions. See session.
- config — Handle GAS configuration. See config.
- gar — Deploy/manage Genero archive (.gar) files. See gar.
- gbc — Deploy/manage Genero Browser Client (GBC). See gbc.
- gwa — Deploy/manage Genero Web Applications (GWA). See gwa
- reset-log — Reconfigure logging for sessions or dispatcher. See reset-log.
- monitoring — Manage GAS monitoring. This command has sub commands:
- send-message — Send messages to connected users (by session/app or globally). See send-message.
- close-session — Gracefully close a specified session. See close-session.
- close-all-sessions — Gracefully close all active sessions. See close-all-sessions.
- service — Manage web services. Service also has sub commands:
- list-invalid lists invalidated services.
- revalidate revalidates an invalidated service.
- disable disables a service.
- enable enables a disabled service.
- list-disabled lists disabled services.
- application — Manage applications. Application also has sub commands:
- disable disables an application.
- enable enables a disabled application.
- list-disabled lists disabled applications.
list-sessions— List active sessions (alias ofsession --list-sessions). See list-sessions.
- options are specific to commands and these are described in the next paragraphs.
- args. Some commands have arguments and these are described in the next paragraphs.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Display the version of the GAS and details about the GAS installation. |
|
|
Displays help for the gasadmin command. |
Syntax 1: session command
gasadmin session [options]- The session command administers GAS sessions (default).
- options are described in Session options.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-h
|
Displays help for the command. |
-q
|
Operates in silent mode. Disables logging. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
--whoami |
Display the kind of dispatcher the GAS is using: httpdispatch, fastcgidispatch, or isapidispatch. See Example: Show dispatcher. |
|
|
Stop (kill) all active sessions by requesting each proxy to stop. The user agent is notified with error messages. |
|
|
Stop the specified session id . The user agent is notified with error messages. See Example: Stop sessions. |
--close-all-sessions
|
The gasadmin session
--close-all-sessions feature is deprecated. Use the gasadmin
close-all-session command instead to close all active sessions. |
--close-session session_id
|
The gasadmin session
--close-session feature is deprecated. Use the gasadmin close-session command
instead to close the specified sessions. |
|
|
Ping all active sessions. See Example: Ping sessions. |
|
|
Ping the specified session id. |
|
|
List all known sessions and display
details of the running applications and web services. See also the gasadmin list-sessions
command. For examples, go to Example: List sessions. |
|
|
List all known sessions identifiers. For examples, go to Example: List session ids. |
|
|
Return a count of the number of active sessions. |
|
|
Clear remaining Linux®/UNIX™ domain sockets, and delete temporary files/directories that may not have been removed at the end of a session. See Example: Cleanup session. |
|
|
Retrieve monitor information for a specified session. Information is displayed in XML format on the standard output. See Example: Monitor session. |
--broadcast-message
message |
The broadcast-message feature is
deprecated. It now displays a message to use the gasadmin send-message command instead, and it exits with a status code of
1. |
--idle-time session_id
|
Return the number of seconds a session is in an idle state (meaning no user activity on all applications and child applications for the given session). See Example: Idle session |
Syntax 2: config command
gasadmin config [options]- The config command handles GAS configuration.
- options are described in Config options.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-h
|
Displays help for the command. |
-q
|
Operates in silent mode. Disables logging. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
|
|
Checks the GAS configuration file (as.xcf) and exits. Errors are displayed to the standard output. See Validate with the gasadmin tool. |
|
|
Explode the GAS configuration into a hierarchy of configuration elements and output to file in XML format, one for each application. |
|
|
Explode the given external configuration file in current directory. See Example: Explode configuration file into an XML file |
|
|
Expand resources and replace with real values. Used
with --configuration-explode or --configuration-explode-external.
See Example: Explode configuration file into XML files |
|
|
Compress the resources located in specified paths. The path separator is a comma (,). See Example: Compress resources. |
--list
|
Lists all applications and services (not just the deployed ones) found in the GAS. |
--xml-output
|
Output result in XML format (for
--list option only). |
Syntax 3: gar command
gasadmin gar [options]- The gar command deploys Genero archives (gar) files.
- options are described in gar options.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Displays help for the gasadmin command. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
--deploy-archive archive_file
|
Unpack the given archive content into the deployment directory. See Deploy an archive with gasadmin |
--undeploy-archive archive_file
|
Undeploy the given archive. See Undeploy an archive with gasadmin |
--enable-archive archive_file
|
Expose all services and applications contained in the given archive. See Enable a deployed archive with gasadmin |
--disable-archive archive_file
|
Unexpose all services and applications contained in the specified archive. See Disable a deployed archive |
--list-archives archive_file |
List all deployed applications in the specified archive or in the list of archives. The entries in the lists are separated by spaces. See List deployed archives |
--clean-archives archive_file
|
Clean up (remove) the specified archive or all the archives provided in a list of archives. The entries in the lists are separated by spaces. See Clean up undeployed archives |
--xml-output
|
Output result of command in XML format. Only compatible with archive options. |
|
|
Shows the deployment path of the given archive. |
|
|
Do not prompt for confirmation. |
Syntax 4: gbc command
gasadmin gbc [options]- The gbc command deploys Genero Browser Client (GBC).
- options are described in gbc options.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Displays help for the gasadmin command. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
--deploy gbc_content
|
Unpack given GBC content into the deployment directory
defined by the res.gbc.deployment resource. See Example: Deploy GBC. |
--undeploy gbc_content
|
Remove the given GBC content. If the undeployed GBC is the current default, the new default will be the one embedded in the FGLGWS package. |
--default gbc_client
|
Set the specified GBC as default client. See Example: list deployed GBC clients and set a default |
--list
|
List all static GBC ( those configured in the as.xcf) and deployed clients on the Genero Application Server. |
--reset
|
Reset to initial delivered GBC in the FGLGWS package. |
--rename old_gbc_name=new_gbc_name
|
Rename the given GBC. Important:
The GBC client set as default, can not be renamed as it may be in use. |
--xml-output
|
Output result of command in XML format. |
Syntax 5: gwa command
gasadmin gwa [options]- The gwa command deploys Genero Web Application.
- options are described in gwa options.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Displays help for the gasadmin command. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
--deploy-archive gwa_filename
|
Unpack given GWA file into the deployment directory
defined by the res.gwa.deployment.root resource. See Example: Deploy GWA. |
--undeploy-archive gwa_filename
|
Remove the given GWA archive. See Example: Undeploy a GWA. |
--list-archives
|
List all deployed GWA on the Genero Application Server. |
--xml-output
|
Output result of command in XML format. |
|
|
Shows the deployment path of the given GWA archive. |
Syntax 6: reset-log command
gasadmin reset-log [options] { dispatcher | session_id [...] | dispatcher session_id [...] } - The reset-log command reconfigures the logs for the running dispatcher and/or for one or more sessions.
- options are described in reset-log options.
- Specify the running dispatcher (using the word "dispatcher") and/or session ids. The session-id is a string that
identifies the session, for example
"
96c9ce0ded72135ddf43ad421a2d87b9". One or more sessions may be specified, separated by spaces.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-h
|
Displays help for the command. |
-q
|
Operates in silent mode. Disables logging. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
--output-type
|
Define where logs are sent (CONSOLE
or DAILYFILE), default is DAILYFILE. In development, with the
standalone GAS (httpdispatch), you can reset log output to the |
--output-path output_dir
|
Define the output directory where the
DAILYFILE log file is stored.If you do not specify an output directory,
gasadmin uses the value defined in the |
--raw-data-max-length max
|
Define the max length of a log message. See RAW_DATA. If you do not
specify the data max length, gasadmin uses the value defined in the
|
--format column-headings
|
Define the columns to output as the format of the log
message. See FORMAT. If you
do not specify the column headings, gasadmin uses the values defined in the
|
--categories category-list
|
Define the log categories to enable. See CATEGORIES_FILTER. If you do
not specify the log categories, gasadmin uses the values defined in the
|
Syntax 7: monitoring status command
gasadmin monitoring status [options] { session-id | service-name }- The monitoring status command gets monitoring configuration status.
- options are described in monitoring status options.
-
The session-id is a string that
identifies the session, for example
"
96c9ce0ded72135ddf43ad421a2d87b9". - The service-name identifies the web service session. Use
group-name/service-namefor non-default groups (for example,demo/Calculator); omit the group for default-group services.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-h
|
Displays help for the command. |
-q
|
Operates in silent mode. Disables logging. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
--session
|
Monitor the status of a specified session. See Quick start: setting monitoring alarms. |
--service
|
Configure monitoring for a service. While you typically include both the group and
the service name using the format " |
--xml-output
|
Output result of command in XML format. |
--file filename
|
Output result of command in the specified file. |
Syntax 8: monitoring update command
gasadmin monitoring update [options] { session-id | service-name }- The monitoring update command sets the monitoring configuration.
- options are described in monitoring update options.
-
The session-id is a string that
identifies the session, for example
"
96c9ce0ded72135ddf43ad421a2d87b9". - The service-name identifies the web service session. Use
group-name/service-namefor non-default groups (for example,demo/Calculator); omit the group for default-group services.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-h
|
Displays help for the command. |
-q
|
Operates in silent mode. Disables logging. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
--session
|
Configure monitoring for a session. See Quick start: setting monitoring alarms. |
--service
|
Configure monitoring for a service. While you typically include both the group and
the service name using the format " |
--enable
|
Enable monitoring. You can enable monitoring by
session id or service name using the gasadmin monitoring update --enable command.
If monitoring a service (with --service option) that it is not yet deployed, the
GAS notifies you of this with a message that the configuration is saved to load once the service is
available. See Enable and disable web service monitoring. |
--disable
|
Disable monitoring. See Enable and disable web service monitoring. |
--level
|
Set the monitoring level to one of the valid options:
ALARM, MIN*, MEDIUM, or HIGH. The default is MIN. Levels are case sensitive. See Change the monitoring level for a session or service. |
--set-alarm
|
Set alarm of given name and optional threshold (for
example, DVM_NOT_STARTED=1)See Configure alarms. |
--unset-alarm alarm-name
|
Remove the alarm of given name. See Unset alarms. |
--list-alarm
|
List all alarm names and types. See Configure alarms. |
--xml-output
|
Output result of command in XML format. |
--file filename
|
Output result of command in the specified file. |
Syntax 9: monitoring reset command
gasadmin monitoring reset [options] { session-id | service-name }- The monitoring reset command resets the monitoring configuration.
- options are described in monitoring reset options.
-
The session-id is a string that
identifies the session, for example
"
96c9ce0ded72135ddf43ad421a2d87b9". - The service-name identifies the web service session. Use
group-name/service-namefor non-default groups (for example,demo/Calculator); omit the group for default-group services.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-h
|
Displays help for the command. |
-q
|
Operates in silent mode. Disables logging. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
--session
|
Reset monitoring for a session. See Reset monitoring |
--service
|
Reset monitoring for a service. While you typically include both the group and
the service name using the format " |
--xml-output
|
Output result of command in XML format. |
--file filename
|
Output result of command in the specified file. |
Syntax 10: monitoring fetch command
gasadmin monitoring fetch [options] session-id- The monitoring fetch command retrieves monitoring data stored in .dat files.
- options are described in monitoring fetch options.
-
The session-id is a string that
identifies the session, for example
"
96c9ce0ded72135ddf43ad421a2d87b9".
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-h
|
Displays help for the command. |
-q
|
Operates in silent mode. Disables logging. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
--xml-output
|
Output result of command in XML format. |
--file filename
|
Output result of monitoring fetch command to file. See Fetch monitoring data. |
Syntax 11: monitoring clean command
gasadmin monitoring clean [options]- The monitoring clean command removes monitoring data stored in .dat files.
- options are described in monitoring clean options.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-h
|
Displays help for the command. |
-q
|
Operates in silent mode. Disables logging. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
--all
|
Remove all monitoring data for all sessions using the --all option on its
own. Or remove all data older than a given number of days using the --all --days
num_days option.session_id is not required when
you specify |
--days num_days [ session_id ]
|
Remove monitoring data older then given number of days starting from today for a given
session id. This option can also be used with the option --all. See Remove monitoring data. |
--file filename
|
Output result of command in the specified file. |
Syntax 12: monitoring preload command
gasadmin monitoring preload [options] command-file- The monitoring preload command configures monitoring from commands stored in a file.
- options are described in monitoring preload options.
- command-file identifies the command file.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-h
|
Displays help for the command. |
-q
|
Operates in silent mode. Disables logging. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
-d
|
Specify the target dispatcher. This option is mandatory as the preload command must be run when the dispatcher is not running. See Configure monitoring with commands file. |
--force
|
Force overwriting of existing configuration. |
--directory
directory-name
|
Specify the command file directory location. |
--file filename
|
Output result of command in the specified file. |
Syntax 13: send-message command
gasadmin send-message [options][ session-id [,...] | application-name [,...] ] message- The send-message command allows an administrator of the GAS to send messages to connected users on the specified applications and sessions, or to connected user on all sessions running in the GAS.
- options are described in Table 14.
-
The session-id is a string that
identifies the session, for example
"
96c9ce0ded72135ddf43ad421a2d87b9". - The application-name identifies the application.
Use
group-name/application-namefor non-default groups (for example,mygroup/myapp); omit the group for default-group applications. - message is the message you want to send to the user-agent,for example, "The server will be shutting down in 10
minutes."
For examples using
send-message, see Send administrative messages to user agents.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Displays help for the gasadmin command. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
|
|
The -s option may be used to send a
message to connected users on the specified sessions. This option can take a comma-separated list of
sessions. For examples using
send-message, see Send administrative messages to user agents. |
|
|
The -a option may be used to send a
message to connected users on sessions of the specified applications. This option can take a
comma-separated list of applications. For examples using
send-message, see Send administrative messages to user agents. |
Syntax 14: close-session command
gasadmin close-session [options][ session-id [,...] | application-name [,...] ]- The close-session command closes the specified applications and sessions gracefully.
- options are described in Table 15.
-
The session-id is a string that
identifies the session, for example
"
96c9ce0ded72135ddf43ad421a2d87b9". - The application-name identifies the application.
Use
group-name/application-namefor non-default groups (for example,mygroup/myapp); omit the group for default-group applications.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Displays help for the gasadmin command. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
|
|
The -s option may be used to close
the specified sessions. This option can take a comma-separated list of sessions. See Example: Close sessions (gracefully). |
|
|
The -a option may be used to close
sessions of the specified applications. This option can take a comma-separated list of applications.
See Example: Close sessions (gracefully). |
|
|
The -m option may be used to forward
a message for display to all user agents on closing the session. The message must be enclosed in
quotes. For examples, see Example: Close sessions (gracefully).
Warning:
Options |
|
|
The -u option may be used to
forward an URL for redirection by all user agents on closing the session. The URL must be enclosed
in quotes. For examples, see Example: Close sessions (gracefully). Warning:
Options |
Syntax 15: close-all-sessions command
gasadmin close-all-sessions [options]- The close-all-sessions command closes all sessions gracefully.
- options are described in Table 16.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Displays help for the gasadmin command. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
|
|
The -m option may be used to forward
a message for display to all user agents on closing the session. The message must be enclosed in
quotes. For examples, see Example: Close sessions (gracefully).Warning:
Options |
|
|
The -u option may be used to forward
an URL for redirection by all user agents on closing the session. The URL must be enclosed in
quotes. For examples, see Example: Close sessions (gracefully).Warning:
Options |
Syntax 16: service list-invalid command
gasadmin service list-invalid [options]- The service list-invalid command lists invalidated services.
- options are described in Table 17.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Displays help for the gasadmin command. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
|
|
Output the result in JSON or text format. The default is text. |
Syntax 17: service revalidate command
gasadmin service revalidate [options] { service-name }- The service revalidate command revalidates an invalid service.
- options are described in Table 18.
- The service-name identifies the web service session. Use
group-name/service-namefor non-default groups (for example,demo/Calculator); omit the group for default-group services.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Displays help for the gasadmin command. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
|
|
Output the result in JSON or text format. The default is text. |
Syntax 18: service disable command
gasadmin service disable [options] { service-name }- The service disable command disables a service.
- options are described in Table 19.
- The service-name identifies the web service session. Use
group-name/service-namefor non-default groups (for example,demo/Calculator); omit the group for default-group services.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Displays help for the gasadmin command. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
|
|
Output the result in JSON or text format. The default is text. |
Syntax 19: service enable command
gasadmin service enable [options] { service-name }- The service enable command enables a disabled service.
- options are described in Table 20.
- The service-name identifies the web service session. Use
group-name/service-namefor non-default groups (for example,demo/Calculator); omit the group for default-group services.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Displays help for the gasadmin command. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
|
|
Output the result in JSON or text format. The default is text. |
Syntax 20: service list-disabled command
gasadmin service list-disabled [options]- The service list-disabled command lists disabled services.
- options are described in Table 21.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Displays help for the gasadmin command. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
|
|
Output the result in JSON or text format. The default is text. |
Syntax 21: application disable command
gasadmin application disable [options] { application-name }- The application disable command disables an application.
- options are described in Table 22.
- The application-name identifies the application.
Use
group-name/application-namefor non-default groups (for example,mygroup/myapp); omit the group for default-group applications.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Displays help for the gasadmin command. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
|
|
Output the result in JSON or text format. The default is text. |
Syntax 22: application enable command
gasadmin application enable [options] { application-name }- The application enable command enables a disabled application.
- options are described in Table 23.
- The application-name identifies the application.
Use
group-name/application-namefor non-default groups (for example,mygroup/myapp); omit the group for default-group applications.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Displays help for the gasadmin command. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
|
|
Output the result in JSON or text format. The default is text. |
Syntax 23: application list-disabled command
gasadmin application list-disabled [options]- The application list-disabled command lists disabled applications.
- options are described in Table 24.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Displays help for the gasadmin command. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
|
|
Output the result in JSON or text format. The default is text. |
Syntax 24: list-sessions command
gasadmin list-sessions [options]- The list-sessions command lists the active sessions.
- options are described in Table 25.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Displays help for the gasadmin command. |
-p directory-name
|
Specify the Genero Application Server directory. |
-f filename
|
Specify the configuration file to use. If not specified, the default configuration file, $FGLASDIR/etc/as.xcf, is used. |
-o
|
Set the output format to one of the valid options, json or text. Default is text. For examples, go to Example: List sessions |
-q
|
Operates in silent mode. Disables logging. |
|
|
Define or overwrite a resource. For examples, go to Override configuration resources |
Examples
Session command examples
Use gasadmin session to inspect and manage sessions on the GAS.
Example: List sessions
List all sessions on the dispatcher.
TCP_ADMIN_PORT) used by the dispatcher for this
purpose. Use -f xcf to specify a non-default config
file:gasadmin session --list-sessionsgasadmin list-sessions is an equivalent alias and produces the same output as
gasadmin session --list-sessions.
- session identifier: identifies the GAS session for the application or web service. In the
example, this is "
96c9ce0ded72135ddf43ad421a2d87b9". Name: represents the name of the application or web service running in the session.Port: represents the port number the uaproxy or gwsproxy is using to communicate with the dispatcher (if UNIX sockets are used, the value is 0).Type: identifies the type of session: "WebServices" or "UA Client" (application).Pid: represents the pid of the uaproxy or gwsproxy.GSID: represents the Genero session id used by web applications. In the example, this is "1a5569ed45193a6abd7a2e8e67199300". The GSID is used by the browser to keep track of the session of a web application. The value is stored in a cookie. GSID is not used by web services.VM Pids: represents the fglrun processes the current uaproxy or gwsproxy has started.
Session list: (httpdispatch)
- 96c9ce0ded72135ddf43ad421a2d87b9
Name: demo/RestBook
Port: 51744
Type: WebServices
Pid : 7708
GSID:
VM Pids:
- 13880
- 17068
- dfd29c347ecf2d572aef95a13c6d4a04
Name: _default/demo
Port: 51732
Type: UA Client
Pid : 8632
GSID: 1a5569ed45193a6abd7a2e8e67199300
VM Pids:
- 8568
- 13880
- 17068
- 6448Example: List session ids
List only session identifiers:
TCP_ADMIN_PORT) used by the dispatcher for this
purpose. Use -f xcf to specify a non-default config
file:gasadmin session list-session-ids Session list:
- 784f51e41e5010db8bc201915fc95fe8
- 906d0e5fc69b196f348fd85d371315cf
- 1d5d88ddf6e2cbfdcd47791583e2c163
- 03d7e82913d590a316fbeb4b1ded6624gasadmin session list-session-ids --quiet784f51e41e5010db8bc201915fc95fe8 906d0e5fc69b196f348fd85d371315cf 1d5d88ddf6e2cbfdcd47791583e2c163 03d7e82913d590a316fbeb4b1ded6624
Example: Ping sessions
Ping all sessions for a given config file:
TCP_ADMIN_PORT) used by the dispatcher for this
purpose. Use -f xcf to specify a non-default config
file:gasadmin session -X -f as1.xcf Checking all sessions: (httpdispatch) Ping session 96c9ce0ded72135ddf43ad421a2d87b9 (demo/RestBook): OK Ping session dfd29c347ecf2d572aef95a13c6d4a04 (_default/demo): OK
Example: Stop sessions
Stop a specific session (by session id):
TCP_ADMIN_PORT) used by the dispatcher for this
purpose. Use -f xcf to specify a non-default config
file:gasadmin session -k d98290172c8f7c0d861db329f1ce6597 -f as1.xcf gasadmin session -KExample: Close sessions (gracefully)
gasadmin close-session --session d98290172c8f7c0d861db329f1ce6597 -f as1.xcf
--message "closed"
gasadmin close-session --session d98290172c8f7c0d861db329f1ce6597 -f as1.xcf
--end-url "http://www.4js.com"The
command is run on the admin port (TCP_ADMIN_PORT) used by the dispatcher for this
purpose. Use -f xcf to specify a non-default config
file:
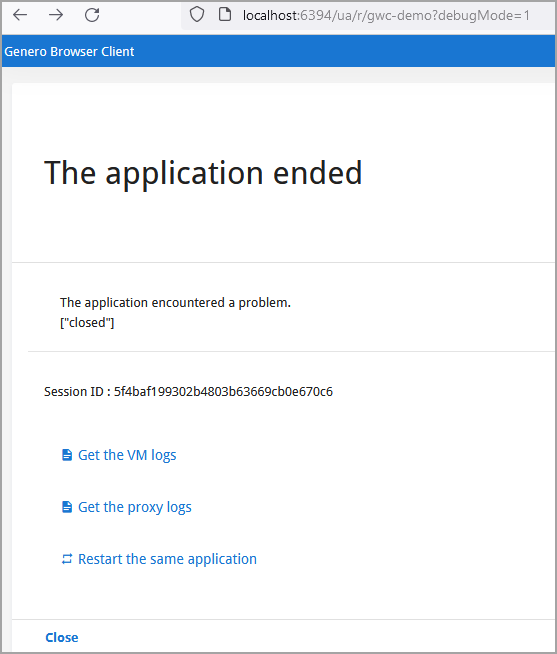
gasadmin close-all-sessions -m "You have been disconnected"
gasadmin close-all-sessions -u "http://www.4js.com"gasadmin close-session --app mygroup/myapp -m "You have been disconnected"
gasadmin close-session --app mygroup/myapp -u "http://www.4js.com"Example: Cleanup session
Run session cleanup now (also done automatically at dispatcher startup):
TCP_ADMIN_PORT) used by the dispatcher for
this purpose.gasadmin session --session-cleanupgasadmin --session-cleanup -d <dispatcher> Example: Show dispatcher
gasadmin session --whoami -f as1.xcfThe
command is run on the admin port (TCP_ADMIN_PORT) used by the dispatcher for this
purpose. Use -f xcf to specify a non-default config
file:
Example: Monitor session
gasadmin session --monitor d98290172c8f7c0d861db329f1ce6597gasadmin --dispatcher <dispatcher> --monitor <session-id> Example: Idle session
gasadmin session --idle-time de7b246d34b550020610f40bbcebe20dIdle time for session de7b246d34b550020610f40bbcebe20d: 496
Deploy with gar example
gasadmin gar command deploys Genero archive (.gar)
files.If you start the dispatcher with the -E option to override
res.appdata.path, you must pass the same override to gasadmin gar
so the archive is deployed to that overridden location.
- Starting the dispatcher:
httpdispatch -E res.appdata.path=/work/tmp/gas/appdata
- Deploying the application:
gasadmin gar -E res.appdata.path=/work/tmp/gas/appdata --deploy-archive myapp.gar
Config command examples
Use gasadmin config to inspect and transform GAS configuration files.
Example: Explode configuration file into an XML file
gasadmin config -t demo/CardExample: Explode configuration file into XML files
gasadmin config -r -t demo/CardExample: Compress resources
gasadmin config -z
$FGLASDIR/app,$FGLASDIR/services,$FGLASDIR/web,$$FGLASDIR/tplGBC command examples
These examples demonstrate common ways to use the gasadmin gbc command to manage
GBC clients.
Example: Deploy GBC
gasadmin gbc --deploy c:\fjs\gbc-projects\gbc-5.00.08\archive\custA.zip Example: list deployed GBC clients and set a default
Use --list to show deployed clients and --default to mark one
as the default:
gasadmin gbc --list gasadmin gbc --default custB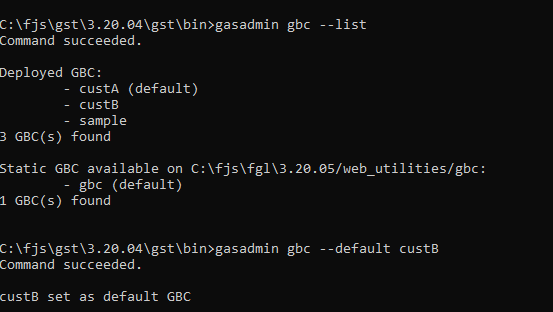
GWA command examples
These examples demonstrate common gasadmin gwa commands for managing Genero Web
Applications (GWA).
Example: Deploy GWA
gasadmin gwa --deploy-archive myapp.gwa Example: Undeploy a GWA
gasadmin gwa --undeploy-archive myapp.gwaReset-log command examples
These examples show common ways to use gasadmin reset-log to reconfigure logging
Example: Reset logs for session
Reset logging for a specific session:
gasadmin reset-log --output-type DAILYFILE --categories "ALL DEBUG" 1170f560ca4d03fd3aa4bbac75da97e9- The
--output-typeoption specifies the logs are sent to the daily log file. - The
--categoriesoption specifies the type of log messages to send; see CATEGORIES_FILTER to view the log type options. - The changes from this command only affect the specified session.Tip:
You can specify multiple sessions by listing the session ids, separated by spaces.
- For unspecified options (for example
--output-path),gasadminfalls back to the LOG configuration inas.xcf; if that is missing (for example,CONSOLEnot configured), default values are used.
Example: Reset logs for dispatcher
gasadmin reset-log --output-type DAILYFILE --categories "ALL DEBUG" dispatcher- Same
--output-type/--categoriesmeanings as above. - Changes apply to the running dispatcher.
Example: Display GAS version information
gasadmin -V Service command examples
Use gasadmin service to inspect and manage services on the GAS.
Example: List invalid services
gasadmin service list-invalid --output jsonRevalidate an invalid service
group-name/service-name for non-default
groups (for example, demo/Calculator); omit the group for default-group services.
gasadmin service revalidate qa-test/bad-serviceList disabled services
gasadmin service list-disabled --output jsonEnable a disabled service
group-name/service-name for non-default
groups (for example, demo/Calculator); omit the group for default-group services.
gasadmin service enable qa-test/svc-3858gasadmin service enable --output json qa-test/svc-3858 Application command examples
Use gasadmin application to inspect and manage applications on the GAS.
List disabled applications
gasadmin application list-disabled --output jsonDisable or enable an application
group-name/application-name for
non-default groups (omit group for default-group apps). To
disable:gasadmin application disable demogasadmin application enable demo