Paged mode of DISPLAY ARRAY
In order to handle very large result sets, use the paged mode of
DISPLAY ARRAY.
Understanding the paged mode
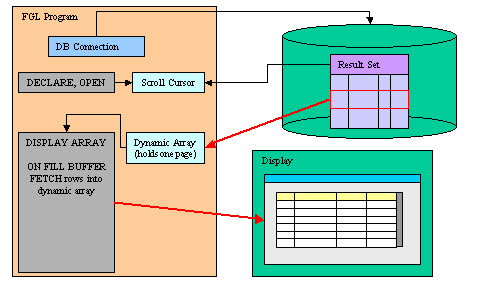
The paged mode of DISPLAY ARRAY allows the program to display a very large number of rows,
without copying all database rows into the program array.
This mode uses the ON FILL
BUFFER data block to let the program populate the array with the current visible
page of rows. This is a subset of the database query result set (SELECT), typically
controlled by a scrollable cursor.
DISPLAY ARRAY has following constraints when using the paged mode:- By default, row sorting is not allowed.
Implement an
ON SORTtrigger to handle list sorting. - Multi-range selection is not supported,
if the paged mode uses an undefined number of rows (
COUNT=-1). - The reduce filter is disapled when using the paged mode.
- To fill a tree view dynamically, use the
ON EXPAND/ON COLLAPSEdata blocks.
Paged mode programming details
In paged mode, the dynamic array holds a page of rows, not all rows of the result
set. The data rows are provided through the ON FILL BUFFER block, by filling a
dynamic array with the rows for the current visible page.
When entering the ON FILL BUFFER block, the dynamic array is already cleared by
the runtime system: It is useless to do a CALL
array-name.clear() before filling the dynamic array.
The ON FILL BUFFER clause is used to fill a page of rows in the dynamic array,
from a row offset and the number of rows required in the page. The row offset is defined by the
fgl_dialog_getbufferstart() built-in function, and the number of rows to
provide is defined by the fgl_dialog_getbufferlength() built-in function.
The ON FILL BUFFER is only triggered when all the user code is executed and the
dialog gets the control back. This means that the fill clause is not immediately fired when calling
DIALOG.setArrayLength().
ON FILL BUFFER block must be executed before the user gets the control:- In a single
DISPLAY ARRAY, theON FILL BUFFERwill be triggered before theBEFORE DISPLAYblock. - In a
DISPLAY ARRAYof aDIALOG/END DIALOGinstruction,ON FILL BUFFERwill be triggered before theBEFORE DIALOGblock.
COUNT dialog attribute of DISPLAY ARRAY:- The total number of rows can be changed during dialog execution with the
ui.Dialog.setArrayLength()method. - In singular
DISPLAY ARRAYinstructions, define the total number of rows of a paged mode with theSET_COUNT()built-in function or theCOUNTattribute. Note thatSET_COUNT()orCOUNTare only taken into account when the dialog starts. - If the total number of rows changes during the execution of the dialog, the only way to specify
the number of rows is
DIALOG.setArrayLength().
DISPLAY ARRAY
dialog, set COUNT=-1 in DISPLAY ARRAY attributes. The dialog will
then query for rows with ON FILL BUFFER until the end of the result set is reached.
The end of the result set is detected:- When the number of rows provided in
ON FILL BUFFERis less than the number of rows required by the dialog. - When you reset the total number of rows to a value higher than -1 with the
ui.Dialog.setArrayLength()method, in the context of theON FILL BUFFERblock.
With paged mode, built-in row sorting is
not supported. Consider setting the UNSORTABLECOLUNMS attribute in the TABLE container, or
implement row sort with the ON SORT trigger.
The dialog cannot support multi-row selection when the total number of rows is undefined.
The DIALOG.setCurrentRow() method can be used to move to a specific row in a
paged mode DISPLAY ARRAY.
Before calling DIALOG.setCurrentRow(screen-array,
row-index), be sure to provide the actual number of rows with DIALOG.setArrayLength(
screen-array, count ) where
count >= row-index. Otherwise, the
setCurrentRow() call will have no effect, if the dialog has not yet seen
row-index rows through ON FILL BUFFER.
If you use a tree view with a paged mode DISPLAY ARRAY, the program will raise
an error at runtime: For tree views, the dialog needs the complete set of open nodes with
parent/child relations to handle the tree view display. With the paged mode, only a short window of
the dataset is known by the dialog.
A typical paged DISPLAY ARRAY implementation consists of a scroll
cursor providing the list of records to be displayed. Scroll cursors use a static
result set. If you want to display fresh data, you can implement an advanced paged
mode by using a scroll cursor that provides the primary keys of the referenced
result set, plus a prepared cursor to fetch rows on demand in the ON FILL
BUFFER clause. In this case you may need to check whether a row still
exists when fetching a record with the second cursor.
Paged mode basic example
DISPLAY ARRAY implementation using a scroll cursor
to fill pages of records in ON FILL BUFFER, specifying an undefined number of rows
(COUNT=-1).MAIN
DEFINE arr DYNAMIC ARRAY OF RECORD
id INTEGER,
fname CHAR(30),
lname CHAR(30)
END RECORD
DEFINE ofs, len, row, i INTEGER
DATABASE stores
OPEN FORM f1 FROM "custlist"
DISPLAY FORM f1
DECLARE c1 SCROLL CURSOR FOR
SELECT customer_num, fname, lname FROM customer
OPEN c1
DISPLAY ARRAY arr TO sr.* ATTRIBUTES(COUNT=-1)
ON FILL BUFFER
LET ofs = fgl_dialog_getBufferStart()
LET len = fgl_dialog_getBufferLength()
LET row = ofs
FOR i=1 TO len
FETCH ABSOLUTE row c1 INTO arr[i].*
IF sqlca.sqlcode==NOTFOUND THEN
EXIT FOR
END IF
LET row = row + 1
END FOR
ON ACTION ten_first_rows_only
CALL DIALOG.setArrayLength("sr", 10)
END DISPLAY
END MAINPaged mode with sorting feature
DISPLAY ARRAY using paged mode, define the
ON SORT block to detect a sort specification change, using the ui.Dialog.getSortKeyAt / ui.Dialog.isSortReverseAt
methods to get sort columns and order, and re-execute the SQL query to sort rows accordingly with an
ORDER BY clause. The ON SORT trigger will be fired before the
ON FILL BUFFER trigger:MAIN
DATABASE test1
OPEN FORM f1 FROM "custlist"
DISPLAY FORM f1
CALL show_list()
END MAIN
FUNCTION execute_sql(order_by)
DEFINE order_by STRING
DEFINE sql STRING
IF order_by IS NULL THEN
LET order_by = "ORDER BY fname"
END IF
LET sql = "SELECT customer_num, fname, lname FROM customer ", order_by
DECLARE c1 SCROLL CURSOR FROM sql
OPEN c1
END FUNCTION
FUNCTION show_list()
DEFINE arr DYNAMIC ARRAY OF RECORD
id INTEGER,
fname VARCHAR(30),
lname VARCHAR(30)
END RECORD
DEFINE ofs, len, row, i INTEGER,
key STRING, rev BOOLEAN,
order_by STRING
CALL execute_sql(NULL)
DISPLAY ARRAY arr TO sr.* ATTRIBUTES(COUNT=-1)
ON SORT
-- Assuming that form field names match table column names
LET i = 1
LET order_by = NULL
WHILE TRUE
LET key = DIALOG.getSortKeyAt("sr",i)
LET rev = DIALOG.isSortReverseAt("sr",i)
IF key IS NULL THEN EXIT WHILE END IF
IF order_by IS NULL THEN
LET order_by = " ORDER BY ", key
ELSE
LET order_by = order_by, ", ", key
END IF
LET order_by = order_by, " ", IIF(rev,"DESC","ASC")
LET i = i + 1
END WHILE
CALL execute_sql(order_by)
ON FILL BUFFER
LET ofs = fgl_dialog_getBufferStart()
LET len = fgl_dialog_getBufferLength()
LET row = ofs
FOR i=1 TO len
FETCH ABSOLUTE row c1 INTO arr[i].*
IF sqlca.sqlcode==NOTFOUND THEN
EXIT FOR
END IF
LET row = row + 1
END FOR
END DISPLAY
END FUNCTIONNote that with the above example, the current row remains at the same position: When the table is
sorted, the set of rows provided in the ON FILL BUFFER may not include the database
row that was the current row before the sort.
DIALOG.setCurrentRow() when the
primary key of the current row is found. The current row might be outside the row set provided in
ON FILL BUFFER. In order to make setCurrentRow() work properly,
you have to count the total number of rows before the DISPLAY
ARRAY: ...
DEFINE cnt, ofs, len, row, i INTEGER,
key STRING, rev BOOLEAN,
row_count, curr_id, last_id INTEGER
...
SELECT COUNT(*) INTO row_count FROM customer
CALL execute_sql(NULL)
DISPLAY ARRAY arr TO sr.* ATTRIBUTES(COUNT=row_count)
ON SORT
LET row = DIALOG.getCurrentRow("sr")
FETCH ABSOLUTE row c1 INTO last_id
-- Here goes code to get sort specification and re-execute SQL
...
LET row=1
WHILE TRUE
FETCH c1 INTO curr_id
IF sqlca.sqlcode==100 THEN
ERROR "Last current row disappeared from result set!"
EXIT PROGRAM 1
END IF
IF curr_id == last_id THEN
CALL DIALOG.setCurrentRow("sr",row)
EXIT WHILE
END IF
LET row = row+1
END WHILE
ON FILL BUFFER
...