Generate service description on demand
The OpenAPI description provides information about the operations defined in a web service.
You can output the OpenAPI description from the URL of the web service in a browser. For details, go to Generate service description on demand (OpenAPI).
When developing client applications that access web services, you may need to refer to the OpenAPI description for the web service for details of the resource endpoints, operations, supported media types, version, scopes, and so on. To learn more about the OpenAPI specification, refer to the OpenAPI documentation.
The sections highlighted in this topic are valuable in respect to Genero RESTful web services. The samples are in JSON format. The output shown is from the Firefox® browser, which converts JSON to human readable format. The output may vary depending on your browser.
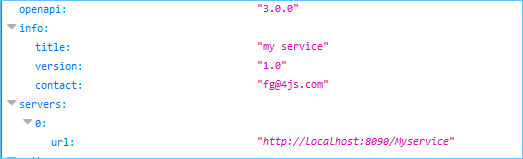
Service information
Paths
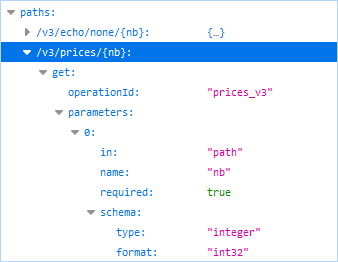
- The URI path (/v3/prices/{nb}). As operations are versioned by URI in this
web service, the version identifier ("
/v3") is displayed as a prefix to the resource path. To read more about versioning, go to Specify version mode.The OpenAPI specification denotes path templates within curly braces (
{ }), and the/{nb}path section of the URI will be substituted with an actual value when a GWS client makes a call to the resource. - The HTTP verb (
get). - The parameters. (Parameters are described in Parameters)
Parameters
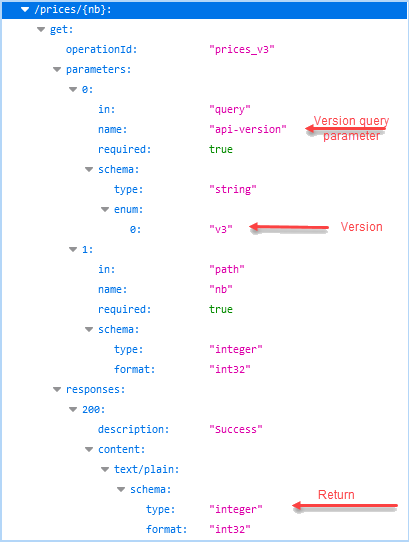
- A query parameter for the version (
api-version) is listed. The version identifier is displayed in the value of theenumkeyword as shown. To read more about versioning, go to Specify version mode. - A path parameter is listed that denotes the
/{nb}path section of the URI, which will be substituted with an actual value when a GWS client makes a call to the resource. - A return parameter is listed under the
responsessection of the operation.
Body requests and responses
POST and PUT HTTP requests usually contain a request body for the payload you want to send to the server. Typically, this will be JSON encoded string.
- If you set WSMedia for
application/xmlas the content type, or the object type is not named in the Genero BDL code (an anonymous or unknown type), the GWS engine exposes the object content like this:- For the request, objects are defined in
propertiesof theschemaof therequestBodysection. - For the response, objects are defined in the
contentsection of theresponsessection.
- For the request, objects are defined in
- If you set
WSMediaforapplication/json(the default) and objects are defined as types (named types) in the Genero BDL code, the GWS engine outputs the type as a reference ($ref) like this:- For the request, the
$refis defined in aschemaof therequestBodysection. - For the response, the
$refis defined in thecontentof theresponsessection.
$refuses an XPath expression to locate where in thecomponents/schemassection of the OpenAPI description the properties are exposed. This named type may be referenced in several resources but only has its properties exposed once. - For the request, the
For information on how Genero BDL data types are mapped in OpenAPI, go to OpenAPI types mapping: BDL.
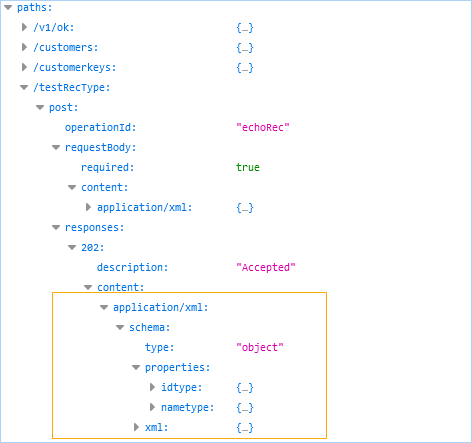
application/xml as the content type; therefore, the
GWS engine exposes the object content (properties) in the schema. 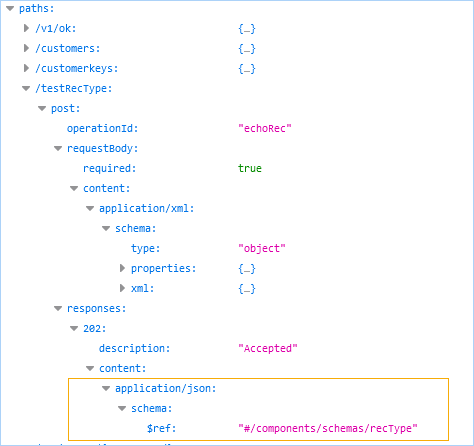
application/json (the default) on a named content
type; therefore, the GWS engine outputs the type as a reference ($ref) in the
schema. A reference definition ($ref) is only allowed in named types used on
a body with a JSON schema. For example, if you set the types for error handling (with
WSError attribute) for application/json (the default), the GWS
engine outputs the type as a reference ($ref) in the responses
section. Parameters like WSHeader, WSQuery, or
WSCookies are not affected.
For a more in-depth understanding of the different parts of OpenAPI descriptions, refer to the OpenAPI documentation.