Quick Start: Generate a Swift report application
Use the Business Application Modeler to generate a Swift report application.
This quick start takes you through the steps for creating a library, where the library code will create the data model in memory and fetch the data one record at a time, sending it to the Genero Report Engine before fetching the next record. The data is streamed as it is fetched, and only one record is held in memory at any time. In addition, a Report Launcher application is generated, allowing you to test your library from within the project. It is assumed that you will take the generated library and use it in your own bespoke applications.
-
Create a new Swift project.
- Select File > New > Swift > BAM Swift Project (.4pw).
-
Enter a name for your project in the Project name field.
This name will become the name of the project workspace file.
- Specify the project directory in the Location field.
-
Click OK.
The project is created and saved in the selected project directory.
Figure: The Default BAM Project for Swift 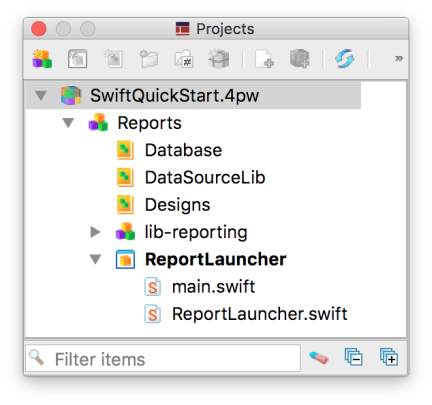
The project is created, to include nodes for database-related files, the data source library files, and the report designs. A ReportLauncher application is created as well, allowing you to test your data source library from within the Genero Studio project.
For a generated Swift project, the lib-reporting group is a library of .swift and .modulemap files that provide the bridge between the Swift code and the C API. These files are not hidden, as you may need to make changes.
-
Add your database meta-schema (.4db) file under
the Database node in the project tree, and save your changes.
If you need to create the database schema (.4db) file, see Create the database meta-schema file.
- Right-click on the Database node and select Add Files.
- Select the meta-schema (.4db) file and click Open.
Figure: Adding the database schema 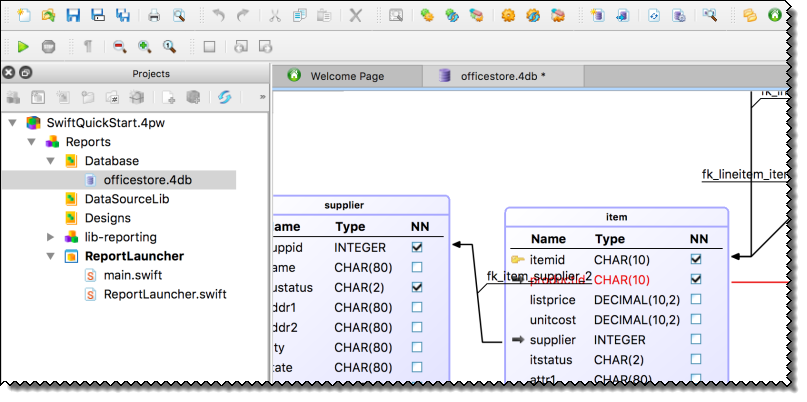
-
Configure the database meta-schema.
In most cases, the database meta-schema will have been created with the tables set to Active and the primary keys defined.
- Open the .4db file.
-
Set the table property for each table you will include to Active.
Tip:
To easily set multiple tables as active, hold down the CTRL key as you select the tables in the Database Structure view, then check the Active property.
- Define a primary key for each table. See Add constraints or indexes.
- Save the changes to your data schema.
-
Create the data source (.4rdj) file.
For this quick start, you will select a single table. Most reporting, however, will involve multiple tables and their relation. See Create a report with BAM for details on creating more complex data sources.
- Select File > New > Swift > Report Data from Database (.4rdj). Click OK.
-
In the Column selection page, select columns from a single table to
include in the record.
The record defines the data that will stream, one record at a time, to the report engine.Click Next > to continue.
- In the Query Creation page, one typically sets the Join, Where and Order by criteria for the data source. As only a single table was selected, this page can be skipped.
-
Click Finish.
A record is created and displayed in a .4rdj tab.
-
Select File >> Save as and save the .4rdj file, adding the file to the DataSourceLib
library node.
Important:
Check the directory before saving your file! It is recommended that you save the file in $(ProjectDir)/src.
Selecting the right name in this step is important; the name of the .4rdj file becomes the name of the Swift source, which ultimately becomes the name of the Swift class. You should choose a name following Swift class naming conventions.Important:Do not use the same name for the record name and the .4rdj file.
- Save the changes to your project.
Figure: Project with data model added 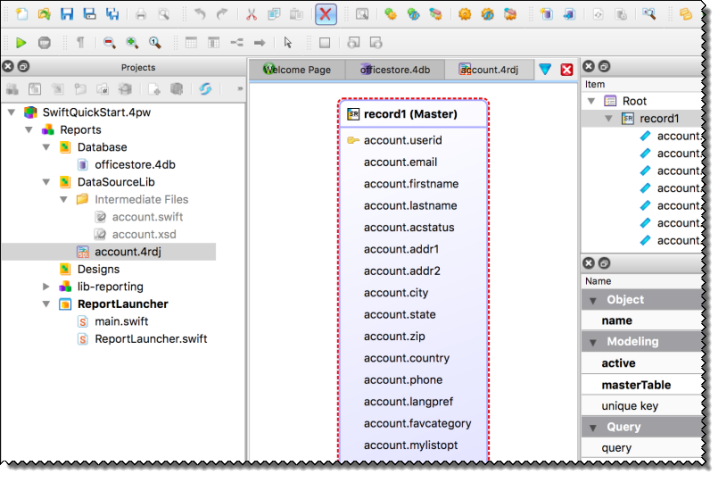
-
Generate the code and the data schema.
-
Right-click the DataSourceLib library node and select
Build.
The DataSourceLib library node is the node containing the data source (.4rdj) file.The report library source and the data schema (.xsd) files are created and listed in the Intermediate Files folder. The location of these intermediate files is determined by the setting of the Target directory property.
-
Right-click the DataSourceLib library node and select
Build.
-
Create a report design from a template.
For this quick start, we are going to use a template to create a simple, non-grouped list report. For more information on using report templates, see Create and manage report templates.
- Select File >> New, Report from Template.
- Select Simple List (PULSE). Click OK.
-
In the Schema location field, select the schema created in the previous step.
The rows field populates for you with the record name. Complete the Repetitions section, mapping the template repetitions to the schema repetitions. Click Next >.
- Add several fields from the Available Fields column to the Selected Fields column. Click Next >.
-
On the Variables page, modify the title placeholder to state
"My Report". Click Finish.
The report is created.
- Select File >> Save untitled.4rp as... and save the file in the $ProjectDir/src directory, and in the Designs node.
Figure: Report added to project 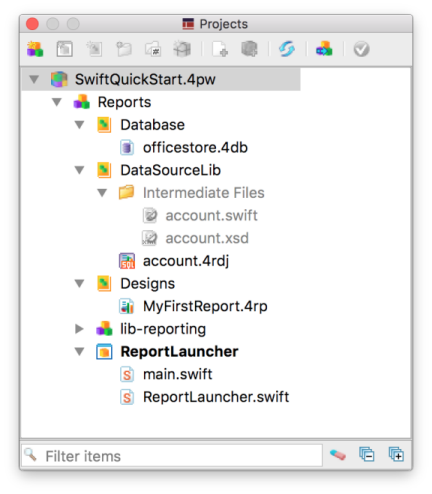
-
Run the Report Launcher application.
-
Select Tools > Genero Tools > Genero Workplace Window. At the prompt, enter:
greportwriter -l 7000. - In the Projects view, select the ReportLauncher application node.
-
Update the Command line arguments to provide the
report details to the application.
The default command line arguments are:
-lib "$(ProjectDir)/bin/libDataSourceLib.dylib" -class "MyReportClass" -design "$(ProjectDir)/src/MyReportDesign.4rp"
Replace"$(ProjectDir)/bin/libDataSourceLib.dylib"with the name of the data source library. This name is the name of your library (in your project) prefixed byliband suffixed by the extension .dylib.Replace
"MyReportClass"with the name of the data source class. This name will be the same as the name of your .4rdj file, without the extension.Replace
"$(ProjectDir)/src/MyReportDesign.4rp"with the path and name of your report. - Right-click the Report Launcher node and select Execute.
The report generates, and is written to a PDF file on disk. See the Output view for the full path to the report file. -
Select Tools > Genero Tools > Genero Workplace Window. At the prompt, enter: