Add/Edit a build rule
From the Build rules dialog you can add or edit a build rule.
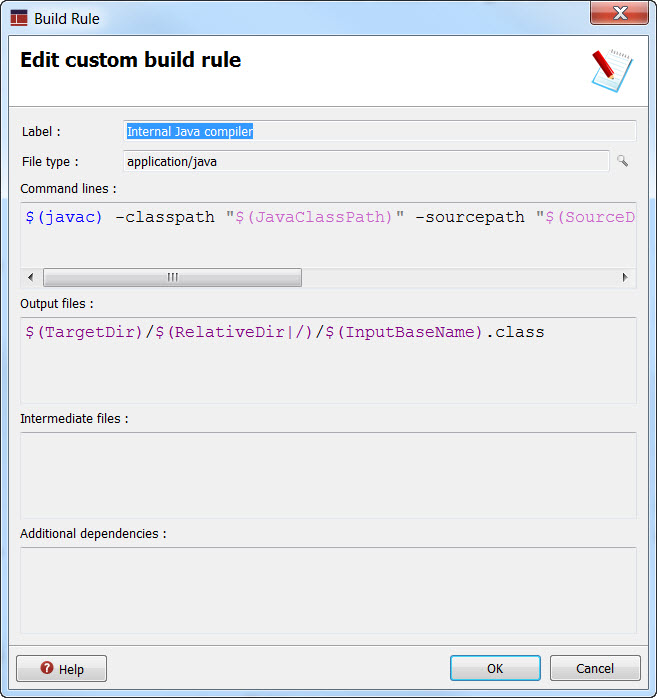
- Label
- Enter a label to be assigned to the rule.
- File type
- Defines the MIME-type of the source files that can be compiled with this Build rule; click the icon on the right to display the File Type Selection dialog. Select the file type from a list generated from the File Associations in Genero Studio Preferences. Use the Search field to limit the display of the list; enter the file extension, or the words Genero or studio, for example, to display only the corresponding file types. The icons can be used to display the list by category, and to expand or contract a category.
- Output files
- Enter the list of files that are generated by the Build rule. All the predefined file node variables can be used when specifying the
path of the file. Note:
When entering file paths, do not use quotations surrounding the file path. That is only necessary in the Command line field.
- Intermediate files
- Indicates which files are generated during compilation, as intermediate files, before generating
the output file. This displays the Intermediate files in the Project view.Note:
When entering file paths, do not use quotations surrounding the file path. That is only necessary in the Command line field.
- Additional dependencies
- The additional dependencies is a list of files used to verify that the build is up to date. If
one of these files has a modified date more recent than any of the output
files, the build is considered not up to date and the build rule will be
executed. Note:
When entering file paths, do not use quotations surrounding the file path. That is only necessary in the Command line field.
Example
For a preprocessor named mypp for source files (*.my), the Build Rule for the mime type "text/my" would be:
For Java:
mypp $(InputPath) -o $(TargetDir)/$(InputBaseName).java
$(javac) -classpath "$(JavaClassPath)" -d "$(TargetDir)" "$(InputDir)/$(InputBaseName).java"
$(delete) $(TargetDir)/$(InputBaseName).javaFor C#:
mypp $(InputPath) -o $(TargetDir)/$(InputBaseName).csFor PHP:
mypp $(InputPath) -o $(TargetDir)/$(InputBaseName).phpFor Swift:
mypp $(InputPath) -o $(TargetDir)/$(InputBaseName).swiftRedirect output
When a command is executed in a build, link, execution rule or in a user action, the output
(standard or error) is displayed in the Output view. You can redirect the output to
a file. For example, if you write echo "Hello World" in a build
rule, Hello World is displayed in the Output view. To
redirect the output to a file, use standard Linux™ syntax such as: echo "Hello World" >
"c:\file.txt". Supported syntax is >,
1>, >>, 2>,
1>&2, 2>&1.