Mobile form patterns
Mobile platforms require special form patterns. These patterns can be modeled in BAM.
Example: Table with 2 actions opens a common CRUD form
Figure: Model of table to grid form pattern
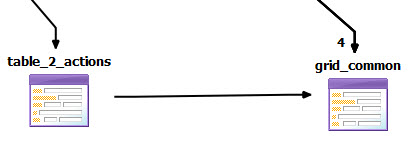
This common mobile pattern can be modeled in BAM by creating a table container form to display the rows and setting a relation to a grid container form for CRUD operations on the individual record selected from the table display.
To see this example model, open the MobilePatterns project from the Welcome Page and open the MobilePatternsAppFlow.4ba file. To run this example, execute MobilePatternsApp to your emulator or device. Select .
On mobile platforms, a table container displays as a list view, not
as a grid with columns. As a list view, it only displays the two first columns' content and any
associated row image. There is no way to manipulate columns (hide, reorder, resize, or sort).
- On two lines for each row.
- On a single line with the first column is left-aligned and the second column is right-aligned. For example, if the first column is a text column (left-aligned) and the second column is a number (right-aligned), they will be rendered on a single line for the row.
If a table is the one and only element in a form, a standard table view displays.
Figure: Running app with table form to grid form pattern
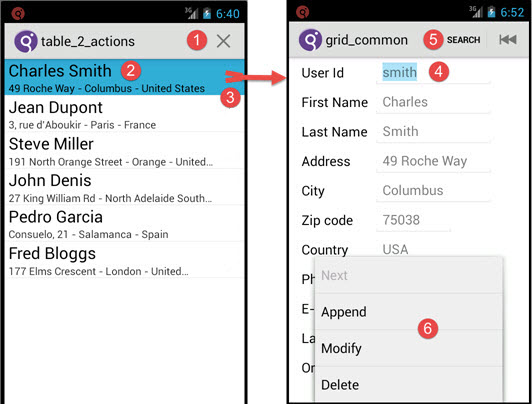
- The table_2_actions form includes a table that has only the
deleteaction code generated. (The record for this form specifies onlycanDeletefunctionality.) The icon or a swipe on the row triggers thedeleteaction. - This table displays rows with two lines on each row. The first column is displayed above the
second column. In the table container definition, two display only columns have been added to the
table to concatenate the first and last name data in the first position and the address data in the
second position. The logic to concatenate the data for these fields has been added as custom code in
a
POINT. See Finding the right place to customize. For example:{<POINT Name="fct.record1_computeFields.user" Status="MODIFIED">} LET l_rec_BRComputedFields.recordfield1 = SFMT("%1 %2", p_br_fields.account_firstname CLIPPED, p_br_fields.account_lastname CLIPPED) LET l_rec_BRComputedFields.recordfield2 = SFMT("%1 - %2 - %3", p_br_fields.account_addr1 CLIPPED, p_br_fields.account_city CLIPPED, p_br_fields.country_codedesc CLIPPED) {</POINT>} - The user can browse the list, delete a selected row, or tap the row to go to a form populated
with the selected record. The
doubleclickproperty on the table specifies the action triggered when the row is selected. In this example the value of thedoubleclickaction isopen_common_form. The code is automatically generated to open the form connected to the table form by a relation in the model.See the Using tables on mobile devices topic in the Genero Business Development Language User Guide for more on table rendering and ergonomics in mobile apps.
- The form opens and displays the correct record. This is achieved by setting some properties on
the relation to the grid form on the BA diagram:
Position, Source Fieldproperty is set toaccount.userid.UI Settings, Actionis set to theopen_common_formaction.UI Settings, Open Modeis set to DISPLAY.
- All CRUD functionality is generated for the grid_common form (search (QBE), read and delete,
create, and update). Available actions display in the order the
ON ACTIONstatements appear in this dialog in the code. Only the first few actions appear in the menu bar at the top, depending on mobile device type. - All other available actions appear when the full menu is displayed by the user (by pressing a menu button on a phone, for example).
Example: Single CRUD forms or Common CRUD form
Figure: Many vs one common form
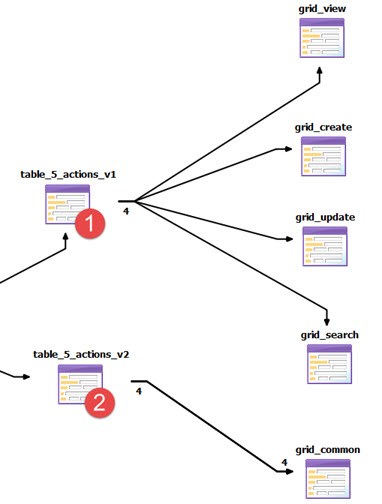
- The table_5_actions_v1 table form calls a different form depending on the action the user triggers. Each form handles a single operation such as (search (QBE), read and delete, create, and update).
- The table _5_actions_v2 table form calls just one form, but models four
different relations to the common form. Each relation opens the form for a different operation such
as (search (QBE), read and delete, create, and update). The
Open ModeandActionproperties are uniquely set on each of the four relations. For example, one of the four relations has theActionproperty set toappendand theOpen Modeproperty set to ADD. When the user triggers theappendaction, the common form is opened and ready to accept input. Furthermore, the ADD Behavior properties on the relation overwrite the form defaults and specify to ExitForm when the user accepts or cancels the input. See Overwriting a Form's behavior with a Relation to the Form