Log test scenario output
Use Log class methods to output errors, warnings, and information from
test scenarios as they play.
In the play method of your Java test scenarios, for example, to have information
about errors, warnings, or debug information displayed as the test is running, add calls to the
log class with the required log method, for example:
runner.log().error("This is bad..."); // for the error
runner.log().warning("Beware !!! "); //for the warning
runner.log().info("Just to tell you..."); //for the info
runner.log().debug("Bug to report..."); //for debug info
public void play(GhostRunner runner)
{
try {
runner.sendAction("INPUT");
ArrayList<FieldInfo> fields = runner.getFields();
for (FieldInfo field : fields) {
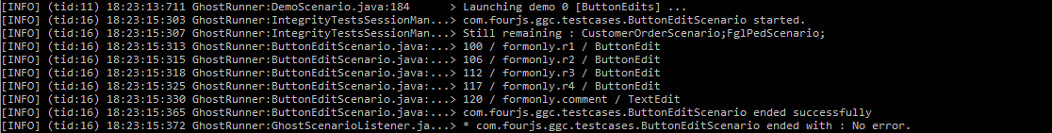
runner.log().info(field.getId(), " / ", field.getName(), " / ", field.getType());
}
runner.sendAction("close");
runner.close();
} catch (GhostException e) {
runner.log().error("ButtonEditDelegatedScenario: exception raised!", e);
} catch (Exception e) {
runner.log().error(e);
}
...
runner.log().info(this.getClass().getName(), " ended successfully");
} runner.sendaction("INPUT"); method selects the INPUT button
of the application. This opens a form for user input.The runner.getFields() method gets details about the form fields; their id,
name, and type. Using the runner.log().info method outputs this information.
In the catch block, any exception raised by the GhostException
method can also be logged as an error by the runner.log().error method.
Figure: ButtonEdit scenario log output
You can adjust the log level with the GHOSTLOG environment variable. This will effect what is outputted to the display. However, it depends on how detailed the logging is in your test play method.