This section outlines the authentication process for an application requiring authentication that is delivered via the Genero Web Client.
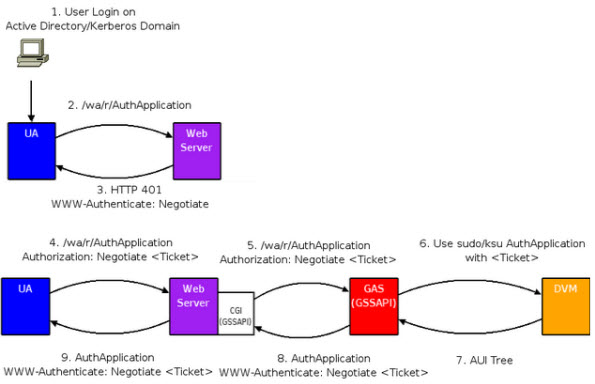
Figure 1. GWC Authentication Process
Authentication Process for a GWC Application:
- User logs on to the domain (such as Active Directory).
- User attempts to access an application from a User Agent (browser), where access to the application is restricted and therefore requires authentication. For example, the user enters the URL for the application, such as http://server.fully.qualified.domain.name:6394/wa/r/AuthApplication.
- User Agent receives an HTTP 401 response from the Web Server asking for authentication credentials. The response header includes: "WWW_Authenticate: Negotiate". An HTTP 401 response code is used when access to a resource is protected and the client did not provide valid authentication credentials.
- The User Agent sends its granted ticket to the Web Server. The response header includes:
"Authorization: Negotiate <Ticket>".At this point, the user is authenticated on the Web
Server.
The Web Server can now relay the request for the application through the GAS Connector.
- The GAS Connector sends the application request to the GAS along with another ticket that authenticates the user to the server. The ticket grants the access to the GAS; no additional login or password information is required.
- The GAS starts the requested application by launching a Dynamic Virtual Machine (DVM) as the
authenticated user.Note: When not using authentication, the DVM is started as the user who started the GAS.
- The DVM sends the AUI tree to the GAS.
- The GAS processes the AUI tree using the Genero Web Client and sends the resulting html page to the GAS Connector.
- The GAS Connector forwards the page to the User Agent.