The architecture of the Genero Application Server uses dispatchers and proxies for optimal reliability, performance and integration in web servers.
The role of the dispatcher is to forward each new incoming request to the appropriate proxy (html5proxy, gwcproxy, gdcproxy, or gwsproxy). The dispatcher handles the GAS configuration and keep a persistent session table of all proxies it has started. In case of failure, the web server restarts the dispatcher, which uses the session table to reconnect to the proxies (and therefore to the applications).
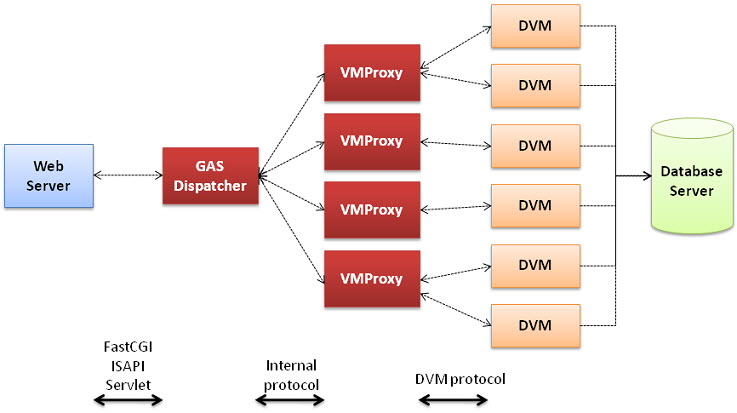
Figure 1. GAS with VMProxy Architecture
Components
- Web Server
- GAS Dispatchers
- VMProxies
- DVMs
- Database Server
How it works: the high-level overview
-
In order to request an application, the end-user enters a URI that specifies which application to surface (based upon the GAS configuration file and application configuration files). For example, the alias to serve up the GWC demo application via a web server would be http://mywebserver/gas/wa/r/gwc-demo.In development environments, it is possible to exclude the Web Server. For more information, see Architecture for Development (Standalone GAS).
-
The Web Server routes the request to the GAS dispatcher. GAS dispatchers refer to the connectors in charge of dispatching a GAS request to the appropriate proxy. There are different GAS dispatchers, each designed for a specific Web Server. For example, the fastcgidispatch.exe is for use with FASTCGI-compliant Web Servers such as Apache, while the isapidispatch.dll is for the Information Internet Services (IIS) Web Server.
-
The GAS Dispatcher starts the VMProxy to handle the request. Each session requesting an application results in a VMProxy starting up; as a result, you will likely see multiple proxies running concurrently. The type of proxy started (html5proxy, gwcproxy, gdcproxy or gwsproxy) will depend on the application being requested. The dispatcher will route to the correct proxy. The dispatcher tracks the session and proxy information in a persistent session table. The presence of this information in the session table ensures that if a dispatcher is killed or restarted, the information needed to return to the proxy and running application is still present. For more information on the responsibilities of the GAS dispatcher, see GAS Dispatcher responsibilities.
-
The VMProxy then launches the DVM for the requested application. It handles any child DVMs, keeps the DVM connections up, and handles the requests and responses appropriate for the type of proxy. For more information of the VMProxy responsibilities, see VMProxy responsibilities.
-
The DVM interacts with the database server, as needed.
GAS Dispatcher responsibilities
The GAS Dispatcher is responsible for:
- Launching VMProxies
- Handling and validating the application or service configuration
- Providing the application configuration to the VMProxy via environment variables
- Handling a persistent and shared session table that manages the forwarding of application requests to the corresponding VMProxies
- Stop the VMProxies when the Web Server shuts down
- Handling static file requests
The GAS Dispatcher is stateless. As a result, you have reliability.
Here the list of dispatchers:
- httpdispatch: standalone dispatcher
- isapidispatch: dispatcher for Internet Information Services
- fastcgidispatch: dispatcher for Fast CGI compliant web servers (like Apache)
- java-j2eedispatch: dispatcher for Java™ Server (like JBoss, Tomcat or WebSphere®)
VMProxy responsiblities
In general, a VMProxy is responsible for:
- Launching the DVM
- Handling child DVMs
- Keeping the DVM connections up
Additional responsibilities depend on the VMProxy type:
- The html5proxy is also responsible for handling HTTP CSF requests, handling the GWC session, and generating the HTML page when the client is the Genero Web Client and the theme is HTML5.
- The gwcproxy is also responsible for handling HTTP CSF requests, handling the GWC session, and generating the HTML page when the client is the Genero Web Client and the theme is any theme other than HTML5 (AJAX, SL, IPHONE, or BASIC).
- The gdcproxy is also responsible for handling HTTP JFE Requests, handling GDC sessions, and generating HTTP JFE responses
- The gwsproxy is also responsible for handling the GWS DVM pool, handling HTTP Web Services requests, and forwarding HTTP Web Services responses (SOAP, REST, XML over HTTP)