Understanding database transactions
This is an introduction to database transactions.
A database transaction delimits a set of database operations (SQL statements), that are processed as a whole.
Database operations included inside a transaction are validated or canceled as a unique operation.
The database server is in charge of data concurrency and data consistency. Data concurrency allows for the simultaneous access of the same data by many users, while data consistency gives each user a consistent view of the database.
Without adequate concurrency and consistency control, data can be changed improperly, compromising integrity of your database. If you want to write applications that can work with different kinds of database servers, you must adapt the program logic to the behavior of the database servers, regarding concurrency and consistency management. This requires good knowledge of multiuser database application programming, transactions, locking mechanisms, isolation levels, and wait mode. If you are not familiar with these concepts, carefully read the documentation of each database server that covers this subject.
Usually, database servers set exclusive locks on rows that are modified or deleted
inside a transaction. These locks are held until the end of the transaction to control
concurrent access to that data. Some database servers implement row versioning
(before modifying a row, the server makes a copy of the original row). This technique allows
readers to see a consistent copy of the rows that are updated during a transaction not yet
committed. When the isolation level is high (REPEATABLE READ) or when using a
SELECT FOR UPDATE statement, the database server sets shared locks
on fetched rows, to prevent other users from changing the rows fetched by the reader. These
locks are held until the end of the transaction. Some database servers allow read locks to
be held regardless of the transactions (WITH HOLD cursor option), but this
is not a standard.
Programs accessing the database can change transaction parameters such as the isolation level or lock wait mode. To write portable applications, you must use a configuration that produces the same behavior on every database engine.
The recommended programming pattern regarding transactions is the following:
- The database must support transactions; this is usually the case.
- Transactions must be as short as possible (a few seconds).
- The isolation level must be at least
COMMITTED READ. - The wait mode for locks must be
WAITorWAIT n(lock timeout).
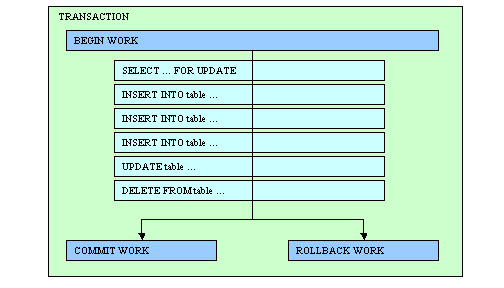
To write portable SQL applications, programmers use the BEGIN WORK, COMMIT WORK and ROLLBACK WORK instructions
described in this section to delimit transaction blocks and define concurrency parameters with SET ISOLATION and SET LOCK MODE. These
instructions are part of the language syntax. At runtime, the database driver generates the
appropriate SQL commands to be used with the target database server. This allows you to use the
same source code for different kinds of database servers.
If you initiate a transaction with a BEGIN WORK statement, you must issue
a COMMIT WORK at the end of the transaction. If one of the SQL statement fails in
the transaction, you typically issue a ROLLBACK WORK to force the database server
to cancel any modifications that the transaction made to the database. If you do not issue a
BEGIN WORK statement to start a transaction, each statement executes within its
own transaction. These single-statement transactions do not require either a BEGIN
WORK statement or a COMMIT WORK statement.
Recent database engines support transaction savepoints, which allows you to set markers in the
current transaction, in order to rollback to a specific point without canceling the complete
transaction. The transaction savepoint instructions SAVEPOINT, ROLLBACK TO
SAVEPOINT and RELEASE
SAVEPOINT are part of the language syntax and can be directly used in the code.
Some database servers do not support a Data Definition Language (DDL) statements (like
CREATE TABLE) inside transactions, and some automatically commit the transaction
when such a statement is executed. Therefore, it is strongly recommended that you avoid DDL
statements inside transactions.
A transaction that processes many rows can exceed the limits that your operating system or the database server configuration imposes on the maximum number of simultaneous locks. Include a limited number of SQL operations in a transaction blocks.
When a program is using several database connections, and if transactions are not terminated before
switching to another connection (SET CONNECTION), it is mandatory to use the
WITH CONCURRENT TRANSACTION option in the CONNECT instruction.