Set a response body and header
You specify a response body in a return parameter without an attribute. Other return values can be sent in headers, using the WSHeader attribute.
A message body in the response is required when you perform an HTTP GET, POST, PUT, DELETE operation on a resource, otherwise the response results in the error-9106.
Example responses in header and body
RETURNS clause has two return values: - An integer is returned in a header. It is specified with the
WSHeaderattribute. - A string is returned in the body. It is specified without an attribute.
PUBLIC FUNCTION help()
ATTRIBUTES (WSGet,
WSPath="/help")
RETURNS (INTEGER ATTRIBUTE(WSHeader, WSDescription="Reference number"),
STRING)
RETURN 3, "Hello world"
END FUNCTION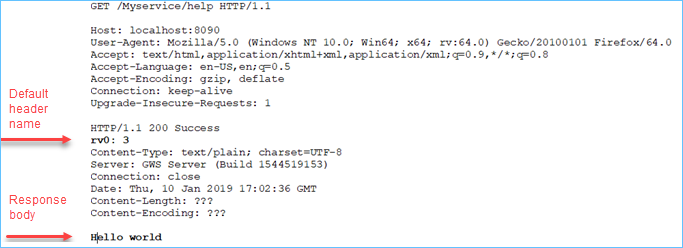
In the output the header is given a default name, "rv0", at runtime. You can change default
header naming via the WSName attribute, for example with:
RETURNS (INTEGER ATTRIBUTE(WSHeader, WSName="MyHeader"), STRING)Setting a
standard HTTP header on a response must be handled with care,
especially for those that define the response body such as Content-Type, or
Content-Encoding. Make sure what you define with WSName does not
conflict with what is specified in the OpenAPI specification for the service.