Understanding parallel dialogs
Parallel dialogs allow the control of several forms simultaneously.
Parallel dialogs use different declarative DIALOG blocks, in
conjunction with the START DIALOG and TERMINATE DIALOG
instructions, and an event loop using the fgl_eventLoop() built-in function, in order to control several forms
simultaneously.
This feature is only for mobile platforms.
Each dialog acts independently to control several elements of a window/form. During the execution
of parallel dialogs, the user can switch to a window/form that is controlled by another running
declarative DIALOG block. For more details about categories of dialogs, see What are dialog controllers?.
INPUT
ARRAY declarative dialogs.The START DIALOG and TERMINATE DIALOG instructions use
declarative dialogs, described in detail in the Declarative dialogs (DIALOG - at module level) chapter.
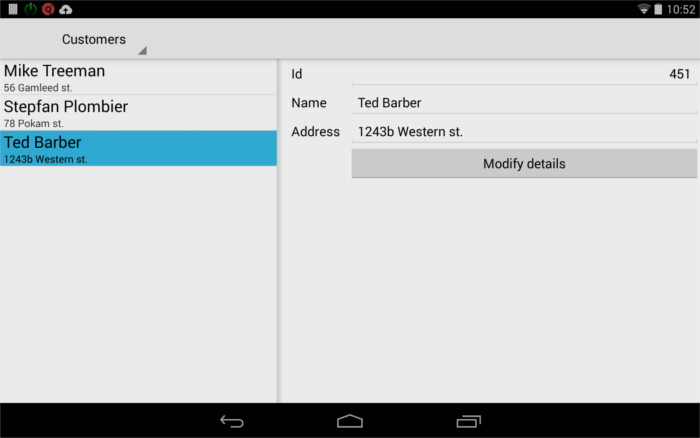
The parallel dialog feature was introduced to implement mobile applications, where several forms can be accessed simultaneously, for example to get "split views" on mobile devices:
In terms of semantics, behavior and control block execution, a declarative dialog started with a
START DIALOG instruction behaves like a procedural DIALOG
block.
UNBUFFERED mode. It is not
possible to change this mode when using parallel dialogs.fgl_eventLoop() built-in function. The minimal event loop code to implement
is:WHILE fgl_eventLoop()
END WHILEOnce the declarative dialogs and the interaction event loop are defined, it is possible to create
the windows with OPEN WINDOW, and initiate the dialogs with the START
DIALOG instruction.
If needed, show a given dialog window with the CURRENT WINDOW instruction.
Additionally, (especially when implementing split views), you may want to "restart" a detail dialog,
for example when selecting a new row in the main record list. To restart the detail dialog, execute
TERMINATE DIALOG, followed by START DIALOG for the detail dialog.
See split view programming for more details.
To finish a given dialog, execute the TERMINATE DIALOG instruction and close the
dedicated window with CLOSE WINDOW window-name.
From a set of running parallel dialogs, it is possible to switch to a modal dialog by creating a dedicated window, and executing a procedural dialog instruction. When the procedural dialog is terminated, close the dedicated window, and the control will go back to the parallel dialog set.