Understanding positioned update or delete
This is an introduction to SQL positionned UPDATE/DELETE.
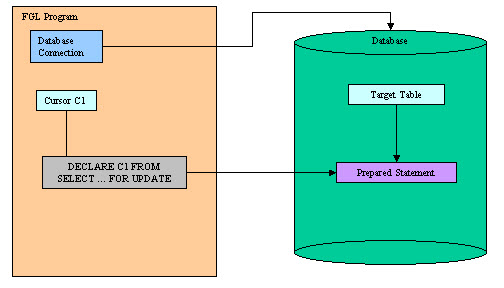
When declaring a database cursor with a SELECT statement using a unique table
and ending with the FOR UPDATE keywords, you can modify the current row pointed by
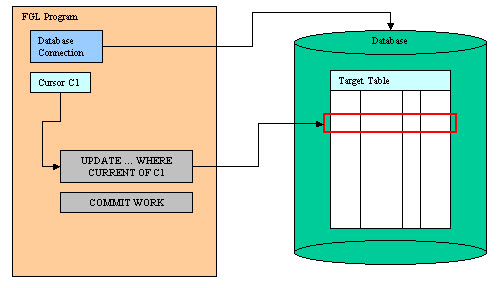
the FOR UPDATE cursor with UPDATE ... WHERE CURRENT
OF, or the current row with DELETE ... WHERE CURRENT
OF statements. Such an operation is called positioned update or
positioned delete.
Do not confuse positioned update with the use of SELECT FOR UPDATE statements
that are not associated with a database cursor. Executing SELECT FOR UPDATE
statements is supported by the language, but you cannot perform positioned updates since there is no
cursor identifier associated with the result set.
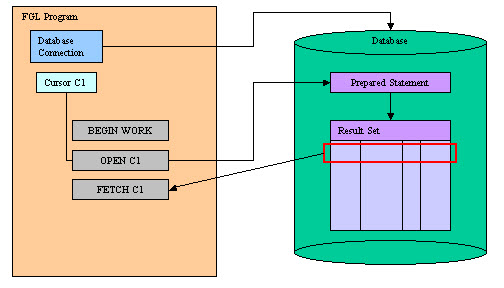
WITH HOLD)
declared with a SELECT statement including the FOR UPDATE
keywords. The SQL standards require for update cursors to be automatically closed at
the end of a transaction. Therefore, it is strongly recommended that you use positioned updates in a
transaction block.To perform a positioned update or delete, perform a DECLARE instruction with a
SELECT FOR UPDATE statement.