Introduction
In a production environment, Genero Web Services becomes a part of a global application architecture handled by the Genero Application Server (GAS). The GWS DVMs are managed by the GAS.
This architecture takes care of:
- Security issues
- Scalability
- Load management
- Balancing of the Web service requests amongst the available virtual machines
- Runtime monitoring
GAS configuration
For deployment, the GWS Server application must be added to the GAS configuration. See Adding Applications in the GAS manual.
The web services application can be added to the GAS in different ways:
-
GWS Server application implementing a single Web Service.
This application could be deployed on various physical machines. A Genero Web Services VMProxy (GWSProxy) is started on each machine where the GWS Server application is executed, to manage the requests for a service and manage the DVMs that handle the requests. A single VMProxy can communication with multiple GWS DVMs, and manage the load balancing.
-
GWS Server application implementing multiple Web Services.
The GWSproxy would manage the client requests, dispatching the request to the appropriate DVM and the appropriate web service.
The basic deployment strategy can be implemented in varying permutations, depending on your business needs and the volume of requests.
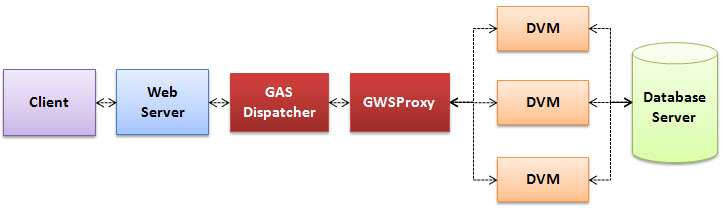
Figure 1. Deployment strategy
-
Using the World Wide Web, a Web Service client requests WSDL information for a particular Web Service from the Web Server.
-
The Web Service client uses this information to make a Web Service request from the Web Server.
-
The Web server passes the request to the GAS dispatcher.
-
The GAS dispatcher starts a GWSProxy, which will be in charge of the pool of DVMs that will serve the web service application.
-
The GWSProxy will start the number of DVMs specified by the START element defined for the web service application.
For a more detailed explanation of the Services Pool for web services, refer to the GAS Architecture topic in the Genero Application Server manual.
Access the web services server from a client application
To reach the web service from the internet, client applications must use the following URL form:
http://host_name/ws/r/app_id
- host_name defines the web server host name where the GAS is running.
- app_id is the XCF file of the GAS web services application.