In order to handle very large result sets, use the paged mode of DISPLAY ARRAY.
Understanding the paged mode
The paged mode of DISPLAY ARRAY allows the program to display a very large number of rows, without copying all database rows into the program array.
This mode uses the ON FILL BUFFER data block to let the program populate the array with the current visible page of rows. This is a subset of the database query result set (SELECT), typically controlled by a scrollable cursor.
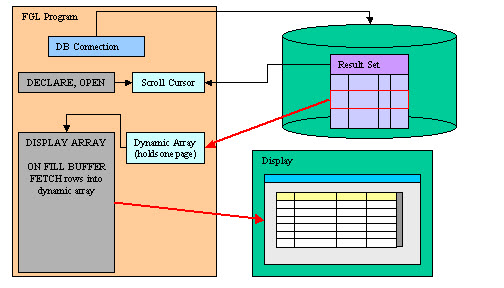
Figure 1. Paged mode diagram
- By default, row sorting is not allowed: Implement an ON SORT trigger to handle list sorting,
- Multi-range selection is not supported, if the paged mode uses an undefined number of rows (COUNT=-1),
- To fill a tree view dynamically, use the ON EXPAND / ON COLLAPSE data blocks.
Paged mode programming details
In paged mode, the dynamic array holds a page of rows, not all rows of the result set. The data rows are provided throught the ON FILL BUFFER block, by filling a dynamic array with the rows of the current page.
If known, specify the total number of rows with the COUNT attribute in the ATTRIBUTES clause of DISPLAY ARRAY. The total number of rows can be changed during dialog execution with the ui.Dialog.setArrayLength() method. In singular DISPLAY ARRAY instructions, you define the total number of rows of a paged mode with the SET_COUNT() built-in function or the COUNT attribute. But these are only taken into account when the dialog starts. If the total number of rows changes during the execution of the dialog, the only way to specify the number of rows is DIALOG.setArrayLength().
If the total number of rows is not known before starting the DISPLAY ARRAY dialog, set COUNT=-1. The dialog will then query for rows until the end of the result set is reached. The end of the result set is detect when the number of rows provided in ON FILL BUFFER are less then the number of rows asked by the dialog, or if you reset the total number of rows to a value higher value as -1 with the ui.Dialog.setArrayLength() method. Note that the dialog cannot support multi-row selection when the total number of rows is undefined.
It is not possible to use treeview decoration when the dialog uses the paged mode: For treeviews, the dialog needs the complete set of open nodes with parent/child relations to handle the tree view display. With the paged mode only a short window of the dataset is known by the dialog. If you use a tree view with a paged mode DISPLAY ARRAY, the program will raise an error at runtime.
A typical paged DISPLAY ARRAY implementation consists of a scroll cursor providing the list of records to be displayed. Scroll cursors use a static result set. If you want to display fresh data, you can implement an advanced paged mode by using a scroll cursor that provides the primary keys of the referenced result set, plus a prepared cursor to fetch rows on demand in the ON FILL BUFFER clause. In this case you may need to check whether a row still exists when fetching a record with the second cursor.
Paged mode basic example
MAIN
DEFINE arr DYNAMIC ARRAY OF RECORD
id INTEGER,
fname CHAR(30),
lname CHAR(30)
END RECORD
DEFINE cnt, ofs, len, row, i INTEGER
DATABASE stores
OPEN FORM f1 FROM "custlist"
DISPLAY FORM f1
DECLARE c1 SCROLL CURSOR FOR
SELECT customer_num, fname, lname FROM customer
OPEN c1
DISPLAY ARRAY arr TO sa.* ATTRIBUTES(COUNT=-1)
ON FILL BUFFER
CALL arr.clear()
LET ofs = fgl_dialog_getBufferStart()
LET len = fgl_dialog_getBufferLength()
LET row = ofs
FOR i=1 TO len
FETCH ABSOLUTE row c1 INTO arr[i].*
IF SQLCA.SQLCODE!=0 THEN
CALL DIALOG.setArrayLength("sa",row-1)
EXIT FOR
END IF
LET row = row + 1
END FOR
ON ACTION ten_first_rows_only
CALL DIALOG.setArrayLength("sa", 10)
END DISPLAY
END MAIN
Paged mode with sorting feature
MAIN
DATABASE test1
OPEN FORM f1 FROM "custlist"
DISPLAY FORM f1
CALL show_list()
END MAIN
FUNCTION execute_sql(order_by)
DEFINE order_by STRING
DEFINE sql STRING
IF order_by IS NULL THEN
LET order_by = "ORDER BY fname"
END IF
LET sql = "SELECT customer_num, fname, lname FROM customer ", order_by
DECLARE c1 SCROLL CURSOR FROM sql
OPEN c1
END FUNCTION
FUNCTION show_list()
DEFINE arr DYNAMIC ARRAY OF RECORD
id INTEGER,
fname VARCHAR(30),
lname VARCHAR(30)
END RECORD
DEFINE cnt, ofs, len, row, i INTEGER,
key STRING, rev BOOLEAN
CALL execute_sql(NULL)
DISPLAY ARRAY arr TO sa.* ATTRIBUTES(COUNT=-1)
ON SORT
LET key = DIALOG.getSortKey("sa")
LET rev = DIALOG.isSortReverse("sa")
IF key IS NULL THEN
CALL execute_sql( NULL )
ELSE
-- Assuming that form field names match table column names
CALL execute_sql( "ORDER BY " || key || IIF(rev," DESC"," ") )
END IF
ON FILL BUFFER
CALL arr.clear()
LET ofs = fgl_dialog_getBufferStart()
LET len = fgl_dialog_getBufferLength()
LET row = ofs
FOR i=1 TO len
FETCH ABSOLUTE row c1 INTO arr[i].*
IF SQLCA.SQLCODE!=0 THEN
CALL DIALOG.setArrayLength("sa",row-1)
EXIT FOR
END IF
LET row = row + 1
END FOR
END DISPLAY
END FUNCTION
Note that with the above example, the current row remains at the same position: When the table is sorted, the set of rows provided in the ON FILL BUFFER may not include the database row that was the current row before the sort.
To track the current row, store the primary key value of the current row before re-executing the query. After query execution, scan the cursor result set and perform a DIALOG.setCurrentRow() when the primary key of the current row is found. The current row might be outside the row set provided in ON FILL BUFFER. In order to make setCurrentRow() work properly, you have to count the total number of rows before the DISPLAY ARRAY: ...
DEFINE cnt, ofs, len, row, i INTEGER,
key STRING, rev BOOLEAN,
row_count, curr_id, last_id INTEGER
...
SELECT COUNT(*) INTO row_count FROM customer
CALL execute_sql(NULL)
DISPLAY ARRAY arr TO sa.* ATTRIBUTES(COUNT=row_count)
ON SORT
LET row = DIALOG.getCurrentRow("sa")
FETCH ABSOLUTE row c1 INTO last_id
LET key = DIALOG.getSortKey("sa")
LET rev = DIALOG.isSortReverse("sa")
IF key IS NULL THEN
CALL execute_sql( NULL )
ELSE
-- Assuming that form field names match table column names
CALL execute_sql( "ORDER BY " || key || IIF(rev," DESC"," ") )
END IF
LET row=1
WHILE TRUE
FETCH c1 INTO curr_id
IF SQLCA.SQLCODE==100 THEN
ERROR "Last current row disappeared from result set!"
EXIT PROGRAM 1
END IF
IF curr_id == last_id THEN
CALL DIALOG.setCurrentRow("sa",row)
EXIT WHILE
END IF
LET row = row+1
END WHILE
ON FILL BUFFER
...