Describes how form item align in grid-based front-ends with an example.
These diagrams show the virtual grid of a complex form, with several field item tags.
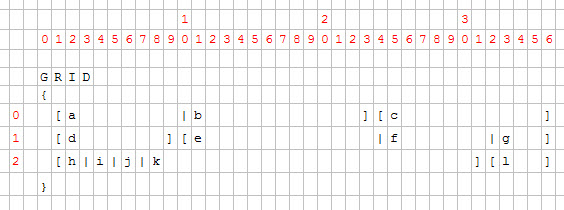
Figure 1. Grid containing several fields
For each form field, the position and the number of cells is computed by the form compiler.
At runtime, the front-end creates the widgets and sets them on the virtual grid.
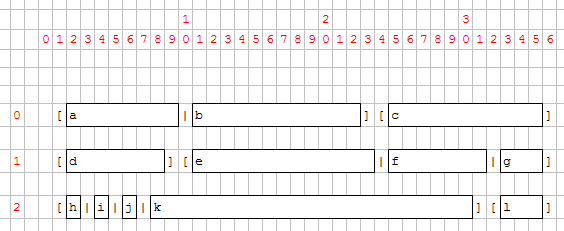
Figure 2. Widgets set on grid
Once widgets are on the grid, their minimum size is computed according to their size, to SIZEPOLICY and the SAMPLE attributes.
Then the sizes of the grid cells adapt to the size of the widgets.
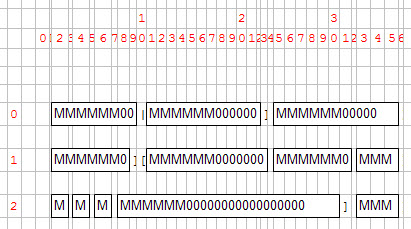
Figure 3. Widget size computations
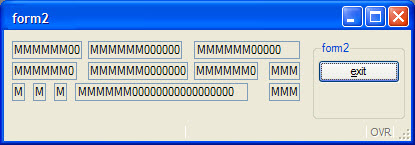
Figure 4. Widgets in rendered form
In this screen shot, the fields k and c are much bigger than expected:
- Field g and l make columns 33, 34 and 35 bigger than the others,
- Field f extends columns 25 to 31.
- As field c has to fill columns 25 to 35, its size grows; the same for field k.
Some fields are proportionally bigger than others because some parameters are variable, while others are fixed.
The width of the widget is the sum of border width, plus the content width (depending on SIZEPOLICY and the SAMPLE attributes).
Since the default SAMPLE is MMMMMM000..., the graphical width of a field is not linearly proportional to the width defined in the form file. For example, a field of 1 will be as wide as 2 borders + 1 'M'. A field of 10 will be as wide as 2 borders + 6 'M' + 4 '0'. This means that a field of 1 is far from being 10 times smaller than a field of 10.