Synchronizing with central database
The database synchronization process involves fetching central changes and sending local updates to the server, ensuring data consistency across users and applications. It includes initializing each synchronization attempt, handling local changes, applying server updates, and managing failures through conflict resolution or database resets.
The sync procedure
When the DB Sync client app is on-line and the sync server can be reached, upon user request
(ON ACTION), or from time to time (ON IDLE), the client app
must fetch central changes and send local changes to the server.
Even if there are no local changes, it is good practice to perform a sync procedure as often as possible when the app is online, to keep the local database up to date with changes done by other users/apps.
Step by step sync process
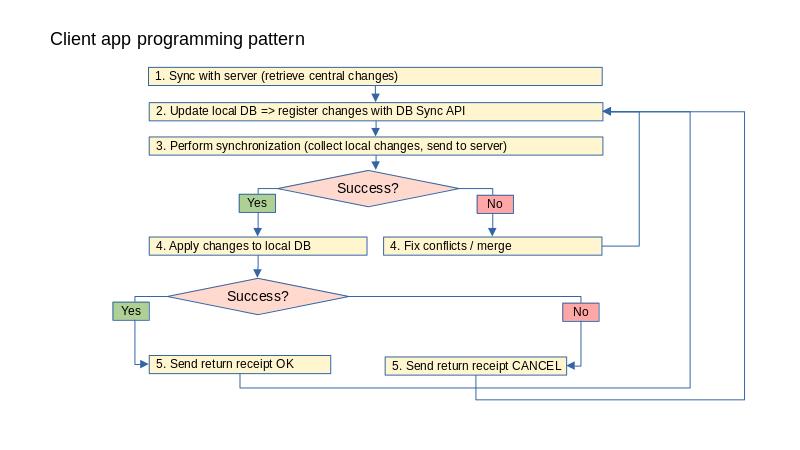
- Initialize the sync procedure:
CALL dbsync_app.data_sync_init( ) CALL dbsync_app.data_sync_set_full_sync( FALSE ) CALL dbsync_app.data_sync_set_return_receipt( TRUE ) -- default after init - Build local primary key lists for each application tables, to let the server collect valid
remaining rows in the central database:
LET s = dbsync_app.collect_local_pkeys() IF s < 0 THEN ... END IF - Collect local changes, for the registered application
tables:
LET s = dbsync_app.collect_local_changes() IF s < 0 THEN ... END IF - Alternatively to steps (2) and (3), if no local changes were registered, you can just ask to
retrieve data for all registered
tables:
CALL dbsync_app.data_sync_retrieve() - Send sync request to the server:
If the database synchronization fails, the server does not expected any return receipt: You must fix issues and re-initiate a new sync process.LET s = dbsync_app.data_sync_send() IF s < 0 THEN ... END IF -
Upon success, apply changes returned by the server, as result events. Result events are available with the
dbsync_app.get_result_events()function:
In case of sync failure, local data changes are still available in the stash table corresponding to the application table:LET s = dbsync_app.apply_data_changes( dbsync_app.get_result_events() ) IF s < 0 THEN ... END IFstash_app-table-nameAfter a clean reset/sync, the data saved in the stash table can be proposed to the end user, to try again the changes after a clean re-sync. -
Send a return receipt to update the last modification timestamp for these tables.
If thedbsync_app.apply_data_changes()function succeeded, you want to send a return receipt withTRUEas last parameter:LET s = dbsync_app.send_return_receipt( TRUE ) IF s < 0 THEN ... END IFUse this function withFALSE, to indicate thatdbsync_app.apply_data_changes()has failed and that you want to fix issues and re-initiate a sync process.Note:This stage is not required, if the return receipt option is disabled with:
However, without return receipt, the server-side cannot be sure that the client has acknoledged and applied the central changes.CALL dbsync_app.data_sync_set_return_receipt( FALSE )
Simplified sync API
dbsync_app.data_sync() function, to implement the synchronization in one single
call:LET s = dbsync_app.data_sync( with-return-receipt-indicator )
IF s < 0 THEN ... END IFPass TRUE or FALSE to indicate that a return receipt must be
used or not.
Handling synchronization failures
A sync failure can typically occur when concurrent users/apps modify the same row, but there can also be a failure when applying central changes into the local database.
To detect sync failures, the DB Sync client app code must check the result status returned by
dbsync_app.data_sync_send(), dbsync_app.apply_data_changes() or
dbsync_app.data_sync(). The exact failure can be identified with the
dbsync_app.get_result_status() function.
The client app code must then resolve conflicts by modifying the local database, based on the errors returned by the DB Sync server, and by using the local data saved in the stash tables.
-
Re-do a complete copy of the database (get filtered rows of tables associated to the user):
-- DISCONNECT from current local SQLite database LET s = dbsync_app.get_database_copy( TRUE, dbfile ) IF s < 0 THEN ... END IF -- CONNECT to new SQLite db in local-db-file -
Do a full-sync (for the registered set of tables, otherwise dbcopy should be faster):
LET s = dbsync_app.data_reset() IF s < 0 THEN ... END IF
In case of sync failure, the easiest option is to save the local changes based on the local sync log and stash tables (for example, in a program array with JSON), reset the local database with a dbcopy or a data reset, then re-apply the saved modifications from scratch by registering all changes, and try a new sync procedure.